Type 2 diabetes mellitus has become an epidemic and major health problem all over the world especially in the Asia Pacific Region. According to the IDF Diabetes Atlas 2013, the prevalence of diabetes in Myanmar is 5.7%.1 The peri-urban diabetes prevalence rate in Myanmar (diagnosed by OGTT) was 11.8% (Urban-13.9%, Rural-7.3%).2 The prevalence of diabetes in Myanmar has shown a rising trend with more urbanization, lifestyle changes including sedentary lifestyle and dietary pattern. According to the World Health Organization, cardiovascular disease is the major cause of morbidity and mortality for individuals with diabetes. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) accounts for 50% of mortality in diabetes. About 25% of patients presenting with myocardial infarction (MI) have diabetes. The risk of death is increased twofold in men and four-to-five fold in women with diabetes.3 Diabetes mellitus is recognized as a risk equivalent for coronary heart disease. The finding of increased cardiovascular risk factors before the onset of type 2 diabetes also suggests that aggressive screening for diabetes combined with improved glycemic control alone will not completely eliminate the excess risk of CHD in type 2 diabetic patients. Clearly, a multifactorial approach to prevention of CHD in type 2 diabetes will be necessary.4
Although the actual data of statin usage in diabetes in Myanmar is not available, it is important to develop a guideline suitable for Myanmar patients with diabetes according to the local situation. These guidelines aim to increase awareness of healthcare practitioners including specialists from various fields such as internists, diabetologists, cardiologists, as well as primary care physicians or general practitioners. These guidelines focus on screening and management of dyslipidaemia mainly in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The task force committee of Myanmar Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism (MSEM) undertook the project to publish evidence based guideline on key issues in management of dyslipidaemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
They were developed by using the best evidence available at the time of guideline development. The evidence grading system for Clinical Practice Recommendations were given grades from A to E (Table1).3
Click here to download Table 1Table 1. The evidence grading system for Clinical Practice Recommendations3

The common conditions coexisting with type 2 diabetes such as hypertension and dyslipidaemia, are clear risk factors for CVD. Insulin resistance in these patients leads to increase prevalence of atherogenic dyslipidaemia.
Type 2 diabetes is associated with a cluster of interrelated plasma lipid and lipoprotein abnormalities including reduced HDL cholesterol, a predominance of small dense LDL particles, and elevated TGL. Low levels of HDL associated with elevated TGL are the most prevalent dyslipidaemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. These changes are also a feature of the metabolic syndrome. Increased LDL levels in diabetics are similar to those found in the general population. There is evidence that each of these lipid alterations is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Numerous randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have shown the efficacy of controlling individual cardiovascular risk factors in type 2 diabetes patients. Aggressive statin therapy reduces cardiovascular end points in patients with DM in both primary and secondary prevention studies.5,6
Screening is important in order to identify patients with suboptimal lipid profiles and then institute corrective measures for either primary or secondary prevention. Annual screening of fasting lipid profile is recommended in most patients with T2DM (B) and should preferably include total cholesterol, HDL, LDL and TG. Direct measurement of LDL cholesterol is preferred. Calculated LDL has problems in patients with high TG levels. Calculated non-HDL (TC-HDL) in moderately elevated TG may provide useful information of the total atherogenic burden. Adults with low-risk lipid values defined by LDL cholesterol <100 mg/dL, HDL cholesterol >50 mg/dL, Triglycerides <150 mg/dL) need repeat lipid assessments every 2 years (E).3 If elevated LDL cholesterol or triglycerides levels are found, clinical and laboratory assessment should be performed in order to rule out secondary causes of dyslipidaemia, such as hypothyroidism, obstructive liver disease, chronic renal disease, drugs and alcohol use (raises triglycerides).
Myanmar diabetes patients are considered to be suitable for target oriented statin therapy. In all persons with T2DM, according to current treatment guidelines, reduction of LDL-C to less than 100 mg/dL is recommend, regardless of baseline lipid levels (B). In very high risk patients in those with DM and established coronary heart disease lowering of LDL-C to less than 70 mg/dL is recommended (B).3
Both medical nutrition therapy (MNT)7 and physical activity8 together with weight loss will lead to decreased triglyceride and increased HDL cholesterol levels and to modest lowering of LDL cholesterol levels as well.
To improve lipid profile in patients with diabetes, lifestyle modification is recommended (A). Lifestyle modification includes increased physical activity and weight reduction, reduced intake of saturated fat, trans fat, and cholesterol, increased consumption of n-3 fatty acids, viscous fiber, plant stanols/sterols.
The targets and recommendations for statin therapy are shown in table 2. Statins should be added to lifestyle therapy, regardless of baseline lipid profile in diabetic patients with overt CVD and those without CVD who are over the age of 40 years and have additional risk factors (hypertension, smoking, family history of CVD, albuminuria, left ventricular hypertrophy, previous cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral vascular disease) (A).
Click here to download Table 2Table 2. Targets and recommendations for statin therapy9

For lower risk patients (e.g., without overt CVD and under the age of 40 years) statin therapy is recommended in addition to lifestyle therapy if LDL remains above 100 mg% or in those with multiple risk factors (C).
If statin treated patients do not reach recommended LDL targets on maximum tolerated doses, reduction of LDL level of 30 to 40% from baseline value is alternative therapeutic goal (B).
Statin therapy is contraindicated in pregnancy (B).
Triglyceride levels <150 mg/dL (1.7mmol/L) and HDL cholesterol >40 mg/dL (1.0 mmol/L) in men and >50 mg/dL (1.3 mmol/L) in women are desirable (C). However, LDL cholesterol-targeted statin therapy remains the preferred strategy (A). The primary target of therapy is LDL cholesterol, unless serum triglycerides are =500 mg/dL. If triglyceride level is more than 500 mg/dl, triglyceride-lowering therapy should be started immediately because of the high risk of pancreatitis.
Individual diabetic patients found to have high triglyceride level should be evaluated for secondary causes including endocrine conditions and medications. Treatment should focus on such secondary causes. In the absence of severe hypertriglyceridemia, therapy targeting HDL cholesterol or triglycerides lacks the strong evidence base compared to statin therapy. Combination therapy has not been shown to provide additional cardiovascular benefit above statin therapy alone and is not generally recommended (A).3
If triglycerides are =200 mg/dL, non-HDL cholesterol becomes the secondary target since VLDL, and especially its remnants, are considered atherogenic.4 It is recommended to set a secondary goal for non-HDL cholesterol (Total - HDL) 30 mg/dL higher than LDL goal. Consider adding a drug to reach non-HDL goal by intensifying therapy with LDL-lowering drug, or adding nicotinic acid or fibrate to further lower VLDL.3
For patients with low HDL cholesterol (<40 mg/dL), consider interventions to raise HDL cholesterol level but only after the goals for LDL cholesterol and non-HDL cholesterol (for patients with triglycerides =200 mg/dL) have been achieved. It is recommended to intensify weight management and increase physical activity. Nicotinic acid or fibrate can also be considered. There is no goal specified for raising HDL in patients with isolated low HDL cholesterol.
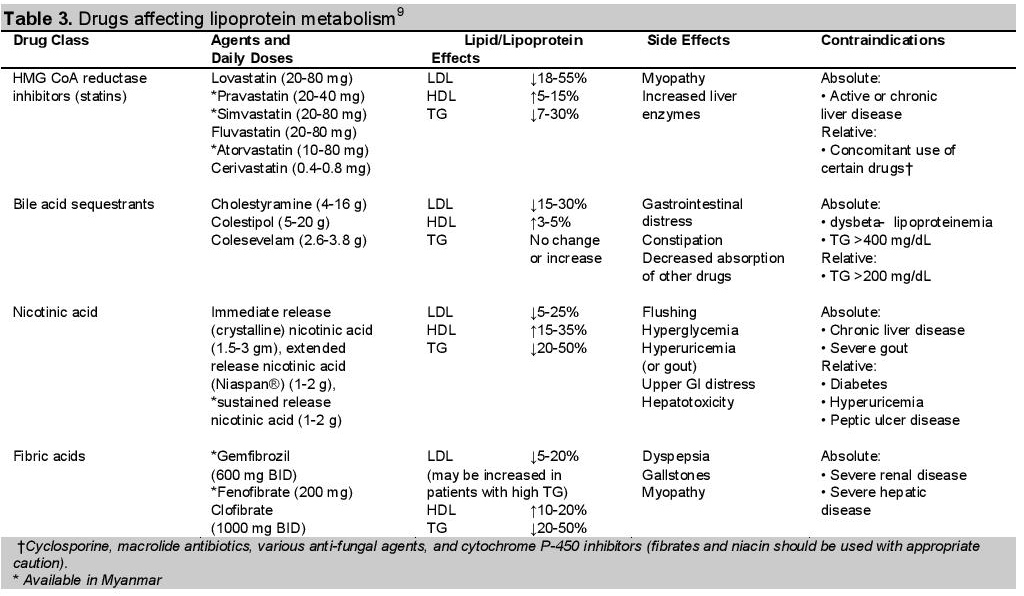
br/>Reassess the patient,s lipid profile 6 weeks after initiation of therapy and again at 6-week intervals until the treatment goal is achieved. Thereafter, patient should be tested at 6 to 12 month intervals. The specific interval should depend on patient adherence to therapy and lipid profile consistency. Liver transaminase levels should be measured before and 3 months after initiation, and whenever lipid altering therapy is restarted, increased, changed or combined. The cholestrol lowering drugs available in Myanmar are mentioned in Table 3.
Click here to download Table 3
Table 3. Drugs affecting lipoprotein metabolism9
A multifactorial approach to prevention of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes is essential, among which management of dyslipidaemia is one of the important strategies. By application of this guideline for the management of dyslipidaemia and proper usage of lipid lowering drugs, by all primary care physicians and specialists, the morbidity and mortality of diabetic patients in Myanmar will be reduced.
1. International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 6th edn. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation, 2013. http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas.
2. WHO step wise approach to NCDs surveillance Myanmar Standard Report (Level 1) 2003-2004.
3. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2014. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37 (Suppl. 1): S14-S80. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc14-S014. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc14-S014.
4. Haffner SM: Management of dyslipidaemia in adults with diabetes (Technical Review). Diabetes Care. 1998;21:160-178.
5. Barrett-Connor E. Diabetes and Heart disease. Diabetes Care.2003;2:2947-58. http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/diacare.26.10.2947.
6. Baigent C, Keech A, Kearney PM, et al.; Cholesterol Treatment Trialists' (CTT) Collaborators. Efficacy and safety of cholesterol lowering treatment: prospective meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomized trials of statins. Lancet. 2005; 366: 1267-1278. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67394-1.
7. American Diabetes Association: Evidence-based nutrition principles and recommendations for the treatment and prevention of diabetes and related complications (Position Statement). Diabetes Care. 2003; 26 (Suppl. 1):S51-S61.
8. American Diabetes Association: Diabetes mellitus and exercise (Position Statement). Diabetes Care. 2001;24:S51-S55.
9. Expert Panel on Blood Cholesterol Levels in Children and Adolescents: Treatment recommendations of the National Cholesterol Education Program Report of the Expert Panel on Blood Cholesterol Levels in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics. 1992;89 (Suppl.):525-584.
Authors are required to accomplish, sign and submit scanned copies of the JAFES Declaration that the article represents original material that is not being considered for publication or has not been published or accepted for publication elsewhere.
Consent forms, as appropriate, have been secured for the publication of information about patients; otherwise, authors declared that all means have been exhausted for securing such consent.
The authors have signed disclosures that there are no financial or other relationships that might lead to a conflict of interest. All authors are required to submit Authorship Certifications that the manuscript has been read and approved by all authors, and that the requirements for authorship have been met by each author.