Single Nucleotide Polymorphism at rs7903146 of Transcription Factor 7-like 2 gene Among Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Myanmar
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15605/jafes.037.S2Keywords:
TCF7L2, SNP, MyanmarAbstract
Objectives. To investigate the association between the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs7903146 in the transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and to examine the impact of this variant on pancreatic beta-cell function in the Myanmar population.
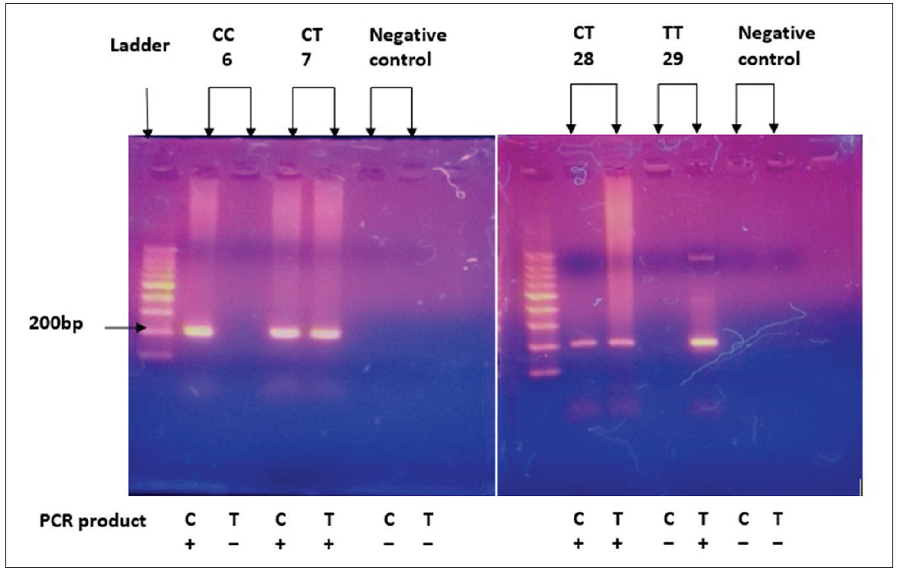
Methodology. A case-control study was undertaken in 100 subjects with T2DM and 113 controls. The SNP rs7903146 was genotyped using the allele-specific polymerase chain reaction method. Plasma glucose and serum insulin levels were determined using the enzymatic colorimetric method and ELISA respectively. Beta-cell function was calculated by the HOMA-β formula.
Results. The frequencies of carrier genotypes (CT and TT) were higher in subjects with T2DM than in controls. The minor T alleles of rs7903146 were found to statistically increase type 2 diabetes risk than the C allele with an allelic odds ratio of 2.07 (95% CI 1.39-3.09, p=0.0004). The mean HOMA-β level of the group with non-carrier genotype (CC) was significantly higher than that of the groups with carrier genotypes (CT and TT) in subjects with T2DM and controls with a p-value of 0.0003 and less than 0.0001, respectively.
Conclusion. The rs7903146 variant of the TCF7L2 gene was found to be associated with T2DM and low β-cell function among Myanmar subjects.
Downloads
References
Kahn CR. Banting lecture. Insulin action, diabetogenes, and the cause of type II diabetes. Diabetes. 1994; 43(8):1066-84. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8039601. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.43.8.1066.
Suzuki K, Akiyama M, Ishigaki K, et al. Identification of 28 new susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population. Nat Genet. 2019;51(3): 379-86. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30718926. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0332-4.
Hayashi T, Iwamoto Y, Kaku K, Hirose H, Maeda S. Replication study for the association of TCF7L2 with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in a Japanese population. Diabetologia. 2007;50(5):980-4. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17340123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-007-0618-z.
Ren Q, Han XY, Wang F, et al. Exon sequencing and association analysis of polymorphisms in TCF7L2 with type 2 diabetes in a Chinese population. Diabetologia. 2008;51(7):1146-52. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18493736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-008-1039-3.
Dabelea D, Dolon LM, Agostino Jr RD, et al. Association testing of TCF7L2 polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes in multi-ethnic youth. Diabetologia; 2011; 54(3):535-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21109996. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3766323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-010-1982-7.
Duval A, Rolland S, Tubacher E, Bui H, Thomas G, Hamelin R. The human T –cell transcriptional factor-4 gene: Structure, extensive characterization of alternative splicings, and mutational analysis in colorectal cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2000; 60(14):3872-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10919662.
Grant SFA, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I, et al. Variant of transcriptional factor 7- like 2 gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2006; 38(3):320-3. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16415884. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1732.
Peng S, Zhu Y, Lü B, Xu F, Li X, and Lai M. TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes risk: A comprehensive and updated meta-analysis involving 121 174 subjects. Mutagenesis. 2013; 28(1): 25-37. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23188737. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/ges048.
Zhou Y, Park SY, Su J, et al. TCF7L2 is a master regulator of insulin production and processing. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(24):6419–31. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25015099. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4240194. https//doi.org/10.1093/ hmg/ddu359.
Cropano C, Santoro N, Groop L, et al. The rs7903146 variant in the TCF7L2 gene increases the risk of prediabetes/type 2 diabetes in obese adolescents by impairing β-cell function and hepatic insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(8):1082-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28611053. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5521977. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc17-0290.
Schäfer SA, Tschritter O, Machicao F, et al. Impaired glucagon-like peptide-1-induced insulin secretion in carrier of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene polymorphisms. Diabetologia. 2007;50(12):2443-50. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17661009. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2063563. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-007-0753-6.
Prestwich TC, Macdouglad OA. Wnt/ beta catenin signaling in adipogenesis and metabolism. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19(6):612-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17997088. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2709272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2007.09.014.
Rulifson IC, Karnik SK, Heiser PW, et al. Wnt signaling regulates pancreatic beta cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007; 104(15):6247-52. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17404238. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1847455. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0701509104.
Barra GB, Dutra LAS, Watanabe SC, et al. Association of the rs7903146 single nucleotide polymorphism at the transcriptional factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) locus with type 2 diabetes in Brazilian subjects. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2012; 56(8): 479-84. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23295285. https://doi.org/10.10590/s0004-27302012000800003.
Yi F, Brubaker PL, Jin T. TCF-4 mediates cell type-specific regulation of proglucagon gene expression by beta-catenin and glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280(2): 1457-64. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15525634. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M411487200.
Lyssenko V, Lupi R, Marchetti P, et al. Mechanisms by which common variants in TCF7L2 gene increase risk of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(8):2155-63. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17671651. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1934596. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI30706.
Ferreira MC, da Silva MER, Fukui RT, Arruda-Marques MdC, Azhar S, Dos Santos RF. Effect of TCF7L2 polymorphism on pancreatic hormones after exenatide in type 2 diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2019; 11:10-19. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ 30700996. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6347826. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-019-0401-6.
World Health Organization and International Diabetes Federation. Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia: Report of a WHO/IDF consultation. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2006. http://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/43588. Accessed December 5, 2010.
Moczulski D, Gawlik B, August R, Strojek K and Grzeszczak W. TCF7L2 gene is associated with type 2 diabetes in Polish population. Exp Clinic Diabetologia, 2007;7(2):109-11.
Thabane L. Sample size determination in clinical trials. HRM-733 Class-Notes. https://www.scribd.com/document/358495328/Thabane-L-Sample-Size-Determination-in-Clinical-Trials-2004-pdf. Accessed by January 20, 2010.
Dutra LAS, Costa PGG, Velasco LFR, Amato AA, Barra GBB. Allele-specific PCR assay to genotype SNP rs7903146 in TCF7L2 gene for rapid screening of diabetes susceptibility. Arg Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 2008; 52(8):1362-6. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19169495. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0004-27302008000800026.
Mayans S, Lockovic K, Lindgren P, et al. TCF7L2 polymorphisms are associated with type 2 diabetes in northern Sweden. Eur J Hum Genet. 2007;15(3):342-6. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17245407. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201773.
Cauchi S, Meyre D, Dina C, et al. Transcription factor TCF7L2 genetic study in the French population: expression in human beta-cells and adipose tissue and strong association with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2006; 55(10):2903-8. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17003360. https://doi.org/10.2337.db06-0474.
Marquezine GF, Pereira AC, Sousa AGP, Mill JG, Hued WA, Krieger JE. TCF7L2 variant genotypes and type 2 diabetes risk in Brazil: Significant association, but not a significant tool for risk stratification in the general population. BMC Med Genet. 2008; 9: 106. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19055834. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2632659. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-9-106.
Chandak GR, Janipalli CS, Bhaskar S, et al. Common variants in the TCF7L2 gene are strongly associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Indian population. Diabetologia, 2007; 50(1):63-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17093941. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-006-0502-2.
Bahaaeldin AM, Seif AA, Hamed AI, Kabiel WAY. Transcription factors 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) rs 7903146 (C/T) polymorphism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Dubai Diabetes Endocrinol J. 2020;26:112-8. https://doi.org/10.1159/000509756.
Elhourch S, Arrouchi H, Mekkaoui N, et al. Significant association of polymorphisms in the TCF7L2 gene with a higher risk of type 2 diabetes in a Moroccan population. J Pers Med. 2021;11(6):461. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34073870. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8225140. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11060461.
Ng MCY, Tam CHT, Lam VKL, So WY, Ma RCW, Chan JCN. Replication and identification of novel variants at TCF7L2 associated with type 2 diabetes in Hong Kong Chinese. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(9):3733-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17609304. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2007-0849.
Pourahmadi M, Erfanian S, Moradzadeh M, Jahromi AS. Non-association between rs7903146 and rs12255372 polymorphisms in transcription factor 7-like 2 gene and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Jahrom City, Iran. Diabetes Metab J. 2015; 39(6): 512-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26616591. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.6.512.
Mandour I, Darwish R, Fayez R, Naguib M, El-Sayegh S. TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus, a pilot study.
Biomedical Pharmacol J. 2018; 11(2): 1043-9. https://doi.org/10.13005/bpj/1465.
Meier JJ, Bonadonna RC. Role of reduced β-cell mass versus impaired β-cell function in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36(2):113-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23882035. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3920783. https://doi.org/10.2337.dcS13-2008.
Loos Ruth JF, Franks PW, Francis RW, Barroso I, Gribble FM, Savage DB. TCF7L2 polymorphisms modulate proinsulin level and beta-cell function in a British Europid population. Diabetes. 2007;56(7):1943-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17416797. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2668957. https://doi.org/10.2337/db07-0055.
Papadopoulou S, Edlund H. Attenuated Wnt signaling perturbs pancreatic growth but not pancreatic function. Diabetes. 2005; 54(10): 2844-51. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16186384. https://doi.org/10.2337.diabetes.54.10.2844.
Takamoto I, Kubota N, Nakaya K, et al. TCF7L2 in mouse pancreatic beta cells plays a crucial role in glucose homeostasis by regulating beta cell mass. Diabetologia. 2014; 57(3): 542–53. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24317852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-013-3131-6
Shu L, Matveyenko A, Kerr-Conte J, Cho JH, McIntosh CHS, Maedler K. Decreased TCF7L2 protein levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus correlate with downregulation of GIP and GLP-1 receptors and impaired beta cell function. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18(13):2388-2399. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19386626. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2722186. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddp178.
da Silva Xavier G, Loder MK, McDonald A, et al. TCF7L2 regulates late events in insulin secretion from pancreatic islet beta cells. Diabetes. 2009;58(4):894-905. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19168596. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2661588. https://doi.org/10.2337/db08-1187.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Sagawah Phu, Aye Thida, Kyu Kyu Maung, Tet Tun Chit

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The full license is at this link: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/legalcode).
To obtain permission to translate/reproduce or download articles or use images FOR COMMERCIAL REUSE/BUSINESS PURPOSES from the Journal of the ASEAN Federation of Endocrine Societies, kindly fill in the Permission Request for Use of Copyrighted Material and return as PDF file to jafes@asia.com or jafes.editor@gmail.com.
A written agreement shall be emailed to the requester should permission be granted.










