Medication Adherence of Persons with Type 2 Diabetes in Malaysia
A Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15605/jafes.037.01.14Keywords:
diabetes mellitus, medication adherence, Malaysia, scoping reviewAbstract
Objective. This is a scoping review of Malaysian scientific studies on medication adherence among persons with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methodology. We conducted a bibliographic search of PubMed, Scopus and Google Scholar using the following keywords: “medication adherence,” “drug compliance,” “DMTAC” and “Malaysia.” The search covered all publications up to 31 December 2021. Eligible articles were original studies conducted in Malaysia that measured or quantified medication adherence among persons with T2DM.
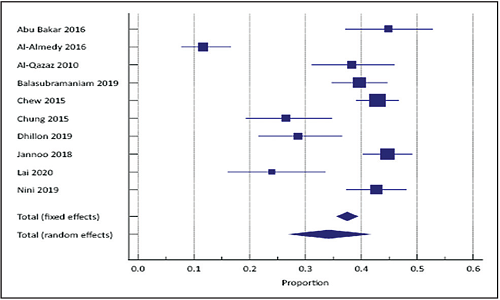
Results. We identified 64 eligible studies published between 2008 to 2021. Most studies included patients with T2DM in ambulatory facilities. Five studies were qualitative research. The quantitative research publications included clinical trials, and cross-sectional, validation, retrospective and prospective cohort studies. Thirty-eight studies used medication adherence scales. The Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8, used in 20 studies) and Malaysian Medication Adherence Scale (MALMAS, used in 6 studies) were the most commonly used tools. There were six validation studies with four medication adherence scales. A meta-analysis of 10 studies using MMAS-8 or MALMAS revealed that the pooled prevalence of low medication adherence is 34.2% (95% CI: 27.4 to 41.2, random effects model). Eighteen publications evaluated various aspects of the Diabetes Medication Therapy Adherence Clinics (DMTAC).
Conclusion. This scoping review documented extensive research on medication adherence among persons with diabetes in Malaysia. The quantitative meta-analysis showed a pooled low medication adherence rate.
Downloads
References
Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(2):88-98. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29219149. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2017.151.
National Health and Morbidity Survey 2019. Shah Alam, Selangor: Institute for Public Health, National Institutes of Health, Ministry of Health, Malaysia; 2020. https://iptk.moh.gov.my/images/technical_report/2020/4_Infographic_Booklet_NHMS_2019_-_English.pdf.
Jan Mohamed HJ, Yap RW, Loy SL, Norris SA, Biesma R, Aagaard-Hansen J. Prevalence and determinants of overweight, obesity, and type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults in Malaysia. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2015;27(2):123-35 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25524952. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010539514562447.
Ganasegeran K, Hor CP, Jamil MFA, et al. A systematic review of the economic burden of type 2 diabetes in Malaysia. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(16) 5723. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32784771. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
PMC7460065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165723.
Protocol Medication Therapy Adherence Clinic: Diabetes, 2nd ed. Petaling Jaya: Pharmaceutical Services Division, Ministry of Health, Malaysia, 2014. https://www.pharmacy.gov.my/v2/sites/default/files/document-upload/buku-protocol-tac-diabetes-fa-ver2_0.pdf.
Dwiputri AW, Pristianty L, Hermansyah A. Pharmacist contributions in the treatment of diabetes mellitus in Southeast Asia: A narrative review. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2020;30(6):1-15. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31971912. https://doi.org/10.1515/jbcpp-2019-0322.
Capoccia K, Odegard PS, Letassy N. Medication adherence with diabetes medication: A systematic review of the literature. Diabetes Educ. 2016;42(1):34-71. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26637240. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145721715619038.
EndNote 20. London: Clarivate Analytics, 2020.
MedCalc® Statistical Software version 20.006. Ostend, Belgium: MedCalc Software Ltd., 2021.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169(7):467-73. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30178033. https://doi.org/10.7326/m18-0850.
Joanna Briggs Institute. Critical appraisal tools Melbourne: University of Melbourne; 2021. https://jbi.global/critical-appraisal-tools.
Abu Bakar Z, Fahrni ML, Khan TM. Patient satisfaction and medication adherence assessment amongst patients at the diabetes medication therapy adherence clinic. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2016;10(2 Suppl 1):S139-43. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27055354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2016.03.015.
Amedy OS, Tang LY, Saido GA. Medication knowledge and adherence among type II diabetes mellitus patients: A cross sectional study. Malays J Nurs. 2018;10(2):24-33. https://doi/org/10.31674/mjn.2018.v10i02.003.
Al-Qazaz HK, Sulaiman SA, Hassali MA, et al. Diabetes knowledge, medication adherence and glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pharm. 2011;33(6):1028-35. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22083724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-011-9582-2.
Balasubramaniam S, Lim SL, Goh LH, Subramaniam S, Tangiisuran B. Evaluation of illness perceptions and their associations with glycaemic control, medication adherence and chronic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in Malaysia. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019;13(4):2585-91. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31405680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2019.07.011.
Chew BH, Hassan NH, Sherina MS. Determinants of medication adherence among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus in three Malaysian public health clinics: A cross-sectional study. Patient Prefer Adher. 2015;9:639-48. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25999699. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
PMC4427255. https://doi.org/10.2147/ppa.s81612.
Chung WW, Chua SS, Lai PS, Morisky DE. The Malaysian Medication Adherence Scale (MALMAS): Concurrent validity using a clinical measure among people with type 2 diabetes in Malaysia. PLoS One. 2015;10(4):e0124275. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25909363. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
PMC4409377. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124275.
Dhillon H, Nordin RB, Ramadas A. Quality of life and associated factors among primary care Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(19):3561. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31547629. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/
PMC6801549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193561.
Jannoo Z, Mamode Khan N. Medication adherence and diabetes self-care activities among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Value Health Reg Issues. 2019;18:30-5. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30419448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vhri.2018.06.003.
Lai PSM, Sellappans R, Chua SS. Reliability and validity of the M-MALMAS Instrument to assess medication adherence in Malay-speaking patients with type 2 diabetes. Pharmaceut Med. 2020;34(3):201-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32436200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40290-020-00335-y.
Nini Shuhaida MH, Siti Suhaila MY, Azidah KA, Norhayati NM, Nani D, Juliawati M. Depression, anxiety, stress and socio-demographic factors for poor glycaemic control in patients with type II diabetes. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2019;14(3):268-76. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31435416. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6695081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2019.03.002.
Abdullah MFILB, Sidi H, Ravindran A, et al. How much do we know about the biopsychosocial predictors of glycaemic control? Age and clinical factors predict glycaemic control, but psychological factors do not. J Diabetes Res. 2020;2020:2654208. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32455131. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7222480. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2654208.
Al Abboud SA, Ahmad S, Bidin MB, Ismail NE. Validation of Malaysian versions of Perceived Diabetes Self-Management Scale (PDSMS), Medication Understanding and Use Self-Efficacy Scale (MUSE) and 8-Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) using Partial Credit Rasch Model. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(11):LC01-5. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28050405. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5198358. https://doi.org/10.7860/jcdr/2016/15079.8845.
Lim PC, Lim K. Evaluation of a pharmacist-managed diabetes medication therapy adherence clinic. Pharm Pract (Granada). 2010;8(4):250-4. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25126149. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4127064. https://doi.org/10.4321/s1886-36552010000400008.
Tan MY, Magarey J. Self-care practices of Malaysian adults with diabetes and sub-optimal glycaemic control. Patient Educ Couns. 2008;72(2):252-67. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18467068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2008.03.017.
Tan MY, Magarey JM, Chee SS, Lee LF, Tan MH. A brief structured education programme enhances self-care practices and improves glycaemic control in Malaysians with poorly controlled diabetes. Health Educ Res. 2011;26(5):896-907. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21715653. https://doi.org/10.1093/her/cyr047.
Akoi C, Rahman MM, Abdullah MS. The relevant intervention strategies for improving medication adherence of diabetic patients. Int J Public Health Res. 2013;3(1):236-40. http://journalarticle.ukm.my/6132/1/vol_3_no_1_2013_31.pdf.
Azmi NL, Mustafa S, Muhamad Nor SH, Mohamad Zalik N. Adherence to prescribed medications among patients with chronic diseases. Int Res J Pharm Med Sci. 2020;3(5):22-6. http://irjpms.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/IRJPMS-V3N5P105Y20.pdf.
Selvadurai S, Makmor-Bakry M, Mhd Ali A. An explorative qualitative study on pharmacist active engagement approach in primary healthcare diabetic education. Indo J Pharm. 2020;31(3):193-204. https://doi.org10.22146/ijp.597.
Yean OB, Zhuang SY, Azmi AN. A prospective cohort study of medication beliefs and their impact on medication adherence in aboriginal and non-aboriginal patients. Malays J Med Health Sci. 2020;16(4):54-63. https://medic.upm.edu.my/upload/dokumen/2020120208290308_MJMHS_0132.pdf.
Sim YC, Mohd-Rosli IS, Lau BT, Ng SY. Patient satisfaction with medication therapy adherence clinic services in a district hospital: A cross-sectional study. Pharm Pract (Granada). 2021;19(2):2353. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34221203. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8221750. https://doi.org/10.18549/pharmpract.2021.2.2353
Al-Qazaz HK, Hassali MA, Shafie AA, Syed Sulaiman SA, Sundram S. Perception and knowledge of patients with type 2 diabetes in Malaysia about their disease and medication: A qualitative study. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2011;7(2):180-91. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21272545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2010.04.005.
Gillani SW, Sulaiman SAS, Abdul MIM, Saad SY. A qualitative study to explore the perception and behavior of patients towards diabetes management with physical disability. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2017;9:58. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28770010. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5525368. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13098-017-0257-6.
Gillani SW, Syed Sulaiman SA, Abdul MIM, Saad SY. Physical disability and diabetes mellitus: Qualitative exploration of patients' perception and behavior. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2018;14(5):472-80. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28699483. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573399813666170710183736.
Saidi S, Milnes LJ. Fatalism, faith and fear: A case study of self-care practice among adults with type 2 diabetes in urban Malaysia. J Clin Nurs. 2018;27(19-20):3758-67. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ 29893043. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.14559.
Al-Qazaz H, Hassali MA, Shafie AA, Sulaiman SA, Sundram S, Morisky DE. The eight-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale MMAS: Translation and validation of the Malaysian version. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;90(2):216-21. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20832888. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3109726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2010.08.012.
Butt M, Mhd Ali A, Bakry MM, Mustafa N. Impact of a pharmacist led diabetes mellitus intervention on HbA1c, medication adherence and quality of life: A randomised controlled study. Saudi Pharm J. 2016;24(1):40-8. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26903767. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4720029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2015.02.023.
Chew BH. Medication adherence on quality of life among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: An exploratory analysis on the EDDMQoL study. Qual Life Res. 2015;24(11):2723-31. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26001640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-015-1006-7.
Chew BH, Mohd Sidik S, Hassan NH. Association of diabetes-related distress, depression, medication adherence, and health-related quality of life with glycated hemoglobin, blood pressure, and lipids in adult patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015;11:669-81. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ 25995640. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4425326. https://doi.org/10.2147/tcrm.s81623.
Chew BH, Vos RC, Pouwer F, Rutten G. The associations between diabetes distress and self-efficacy, medication adherence, self-care activities and disease control depend on the way diabetes distress is measured: Comparing the DDS-17, DDS-2 and the PAID-5. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;142:74-84. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29802952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2018.05.021
Chow EP, Hassali MA, Saleem F, Aljadhey H. Effects of pharmacist-led patient education on diabetes-related knowledge and medication adherence: A home-based study. Health Educ J. 2015;75(4):421-33. https://doi.org/10.1177/0017896915597021.
Hammad MA, Mohamed Noor DA, Syed Sulaiman SA. The effect of patients’ adherence on HbA1c control. Arch Med Pharm Sci Res. 2017;1(1):30-5.
Jannoo Z, Wah YB, Lazim AM, Hassali MA. Examining diabetes distress, medication adherence, diabetes self-care activities, diabetes-specific quality of life and health-related quality of life among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. J Clin Transl Endocrinol. 2017;9:48-54. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29067270. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5651286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcte.2017.07.003.
You LX, Selvadurai S, Yee CK, , et al. Impact of pharmacist-managed diabetes medication therapy adherence clinic (DMTAC) in government health clinics. Malays J Pharm Sci. 2015;13(1):43-51. http://web.usm.my/mjps/mjps13012015/mjps13012015_4.pdf.
Tai CW. An evaluation on pharmacist-managed diabetes medication therapy adherence clinic (DMTAC) in primary health clinic of Johor Bahru district, Malaysia. Johor Health J. 2016;12:41-53.
Butt M, Ali AM, Bakry MM. Concurrent and longitudinal association between glycemic control and self reported medication adherence among type 2 diabetes patients at a tertiary care hospital in Malaysia. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019;15(5):402-6. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30156163. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573399814666180828152754.
Chung WW, Chua SS, Lai PS, Chan SP. Effects of a pharmaceutical care model on medication adherence and glycemic control of people with type 2 diabetes. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2014;8:1185-94. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25214772. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4159395. https://doi.org/10.2147/ppa.s66619.
Maruan K, Md Isa KA, Sulaiman N, Karuppannan M. Adherence of patients with type 2 diabetes to refills and medications: A comparison between ‘telephone and collect’ and conventional counter services in a health clinic. Drugs Ther Perspect. 2020;36:590–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40267-020-00776-0.
Sui CF, Chong TWS, Yip KY, Appalasamy M, Subramaniam AN, Mohan KV, et al. Adherence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients towards antidiabetic medications (ADM) at outpatient department, Hospital Tapah: A cross sectional study using Adherence to Refills and Medications Scale for Diabetes (ARMS-D). Perak Med J. 2021. https://myjms.mohe.gov.my/index.php/pmj/article/view/8167.
Abdullah NF, Khuan L, Theng CA, Sowtali SN, Juni MH. Effect of patient characteristics on medication adherence among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional survey. Contemp Nurse. 2019;55(1):27-37. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30764733. https://doi.org/10.1080/10376178.2019.1583067.
Ahmad NS, Islahudin F, Paraidathathu T. Factors associated with good glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig. 2014;5(5):563-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25411625. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4188115. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12175.
Ahmad NS, Ramli A, Islahudin F, Paraidathathu T. Medication adherence in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated at primary health clinics in Malaysia. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2013;7:525-30. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23814461. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3693921. https://doi.org/10.2147/ppa.s44698.
Azmi NL, Md Rosly NA, Tang HC, Che Darof AF, Zuki ND. Assessment of medication adherence and quality of life among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a tertiary hospital in Kelantan, Malaysia. J Pharm. 2021;1(2):79-86. https://doi.org/10.31436/jop.v1i2.66.
Selvadurai S, Cheah KY, Ching MW, et al. Impact of pharmacist insulin injection re-education on glycemic control among type II diabetic patients in primary health clinics. Saudi Pharm J. 2021;29(7):670-6. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34400860. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8347656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2021.04.028.
Yong SY, Goh GM, Loh HH. Insulin adherence and the associated factors among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at the Hospital Queen Elizabeth II, Sabah. J Public Health. 2020:1-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-020-01409-6.
Gillani SW, Ansari IA, Zaghloul HA, et al. Predictors of health-related quality of life among patients with type II diabetes mellitus who are insulin users: A multidimensional model. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2019;90:53-60. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31193026. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6514425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.curtheres.2019.04.001.
Hatah E, Rahim N, Makmor-Bakry M, et al. Development and validation of Malaysia Medication Adherence Assessment Tool (MyMAAT) for diabetic patients. PLoS One. 2020;15(11):e0241909. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33157549. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7647074. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241909.
Goh SSL, Lai PSM, Liew SM, Tan KM, Chung WW, Chua SS. Development of a PATIENT-Medication Adherence Instrument (P-MAI) and a HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONAL-Medication Adherence Instrument (H-MAI) using the nominal group technique. PLoS One. 2020;15(11):e0242051. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33175871. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7657514. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0242051.
Ting CY, Ahmad Zaidi Adruce S, et al. Effectiveness of a pharmacist-led structured group-based intervention in improving medication adherence and glycaemic control among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A randomized controlled trial. Res Social Adm Pharm. 2021;17(2):344-55. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32327398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2020.03.026.
Ishak NH, Mohd Yusoff SS, Rahman RA, Kadir AA. Diabetes self-care and its associated factors among elderly diabetes in primary care. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2017;12(6):504-11. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31435286. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6694907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2017.03.008.
Jamaludin TSS, Mohammad NM, Hassan M, Nurumal MS. Knowledge and practice on medication adherence among type II diabetes mellitus patients. Enferm Clin. 2021;31(Suppl 2):S372-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enfcli.2020.09.028.
Nasir NM, Ariffin F, Yasin SM. Physician-patient interaction satisfaction and its influence on medication adherence and type-2 diabetic control in a primary care setting. Med J Malays. 2018;73(3):163-9. http://www.e-mjm.org/2018/v73n3/medication-adherence.pdf.
Lim PC, Chung YY, Tan SJ, et al. Comparing the cost, glycaemic control and medication adherence of utilizing patients' own medicines (POMs) versus usual dispensing among diabetic patients in an outpatient setting. Daru. 2021;29(1):125-32. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33538999. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8149523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40199-021-00389-6.
Rosli MR, Neoh CF, Wu DB, Hassan NW, Mahmud M, Rahimi A, et al. Evaluation of home medication review for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus by community pharmacists: A randomised controlled trial. Pharm Pract (Granada). 2021;19(3):2397. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34621450. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8455124. https://doi.org/10.18549/PharmPract.2021.3.2397.
Tey SW, Ibrahim MN, Ahmad R, Alias NM, Zahid MA. An evaluation of the impact of diabetes medication therapy adherence clinic (DMTAC) in Tangkak. Pharm Res Rep. 2020;3(1):35-41. https://research.pharmacy.gov.my/system/files/PRR3.1pp.35-41.pdf.
Alison C, Anselm S. The effectiveness of diabetes medication therapy adherence clinic to improve glycaemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomised controlled trial. Med J Malaysia. 2020;75(3):246-53. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32467540.
Iqbal MZ, Khan AH, Sulaiman SAS, Ibrahim A, Azmi N, Iqbal MS, et al. Effect of pharmacist-led Intervention on progression of diabetic complications at two tertiary care hospitals of Malaysia. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021;13(2):193-8. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34349479. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8291114. https://doi.org/10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_488_20.
Iqbal MZ, Khan AH, Sulaiman SAS, et al. Impact of pharmacist educational intervention on predictors of diabetic retinopathy among diabetic patients at two tertiary care hospitals in Malaysia. Lat Am J Pharm. 2021;40(4):682-9.
Iqbal MZ, Khan AH, Sulaiman SAS, et al. Pharmacist-led educational interventions on determinants of diabetic nephropathy among diabetic patients in Malaysia. Lat Am J Pharm. 2021;40(5):957-64.
Karunagaran L, Dewi LKM, Yee LH. Evaluation on the impact of diabetes – medication therapy adherence clinic (Diabetes-mtac) towards management of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Int J Med Toxicol Leg Med. 2018;21(3-4):162-6. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-4614.2018.00058.X.
Khan AH, Iqbal MZ, Syed Sulaiman SA, Ibrahim A, Azmi N, Iqbal MS, et al. Impact of pharmacist-led educational intervention on predictors of diabetic foot at two different hospitals of Malaysia. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021;13(1):108-15. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34084056. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8142923. https://doi.org/10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_475_20.
Khan AH, Iqbal MZ, Syed Sulaiman SA, Ibrahim A, Binti Yusoff Azmi NS, Iqbal MS. Effect of pharmacist-led intervention on predictors of diabetic neuropathy at two different hospitals of Malaysia. J Pharm Pharmacogn Res. 2021;9(2):153-64.
Lau BT, Ismail SZ, Ng SY, Mohmmad N. Impact of pharmacist-led diabetes program on glycated hemoglobin and diabetes-related hospitalizations in a district-level hospital: A pilot retrospective cohort study. International Journal of Advancement in Life Sciences Research. 2018;1(2):26-36. https://doi.org/10.31632/ijalsr.2018v01i02.005.
Lim PC, Lim K, Embee ZC, Hassali MA, Thiagarajan A, Khan TM. Study investigating the impact of pharmacist involvement on the outcomes of diabetes medication therapy adherence program Malaysia. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2016;29(2):595-601. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27087103.
Morisky Medication Adherence Scale. http://www.moriskyscale.com/.
De Las Cuevas C, Peñate W. Psychometric properties of the eight-item Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (MMAS-8) in a psychiatric outpatient setting. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2015;15(2):121-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30487829. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6224788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijchp.2014.11.003.
Moon SJ, Lee WY, Hwang JS, Hong YP, Morisky DE. Accuracy of a screening tool for medication adherence: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale-8. PLoS One. 2017;12(11):e0187139. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29095870. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5667769. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187139.
Azharuddin M, Adil M, Sharma M, Gyawali B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of non-adherence to anti-diabetic medication: Evidence from low- and middle-income countries. Int J Clin Pract. 2021:75(11):e14717. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34378293. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.14717.
Kennedy-Martin T, Boye KS, Peng X. Cost of medication adherence and persistence in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a literature review. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2017;11:1103-17. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28721024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5501621. https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S136639.
Jaam M, Awaisu A, Ibrahim MI, Kheir N. Synthesizing and appraising the quality of the evidence on factors associated with medication adherence in diabetes: A systematic review of systematic reviews. Value Health Reg Issues. 2017;13:82-91. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29073997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vhri.2017.09.001.
van Eikenhorst L, Taxis K, van Dijk L, de Gier H. Pharmacist-led self-management interventions to improve diabetes outcomes. A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:891. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29311916. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5735079. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00891.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
The full license is at this link: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/legalcode).
To obtain permission to translate/reproduce or download articles or use images FOR COMMERCIAL REUSE/BUSINESS PURPOSES from the Journal of the ASEAN Federation of Endocrine Societies, kindly fill in the Permission Request for Use of Copyrighted Material and return as PDF file to jafes@asia.com or jafes.editor@gmail.com.
A written agreement shall be emailed to the requester should permission be granted.










