Development of a Validated Diabetes Risk Chart as a Simple Tool to Predict the Onset of Diabetes in Bogor, Indonesia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15605/jafes.037.01.09Keywords:
diabetes screening, risk factors, diabetes, cohort study, BogorAbstract
Objective. To develop a simple, non-invasive tool for predicting the onset of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methodology. A total of 4418 nondiabetic respondents living in Bogor were included in this cohort study. Their ages ranged from 25 to 60 years old and were followed for 6 years with interviews, physical examinations and laboratory tests. The investigators used logistic regression to create a tool for diabetes risk determination.
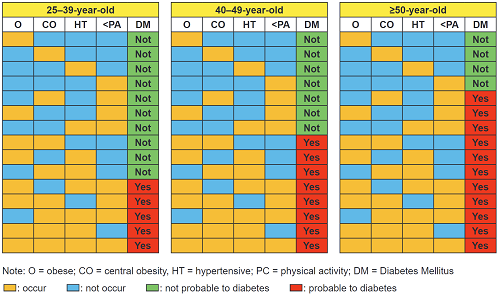
Results. The cumulative incidence of T2DM was 17.9%. Risk factors significantly associated with T2DM included age, obesity, central obesity, hypertension and lack of physical activity. The Bogor Diabetes Risk Prediction (BDRP) chart had a cut-off of 0.128, with sensitivity of 76.6% and specificity of 50.3%. The Positive Predictive Value (PPV) was 21.6% and Negative Predictive Value (NPV) was 92.3%. The Area under the Curve (AUC) was 0.70 with a 95% confidence interval ranging from 0.675-0.721.
Conclusion: The BDRP chart is a simple and non-invasive tool to predict T2DM. In addition, the BDRP chart is reliable and can be easily used in primary health care.
Downloads
References
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 2019 , 9th ed. https://www.idf.org/e-library/epidemiology-research/diabetes-atlas/159-idf-diabetes-atlas-ninth-edition-2019.html.
Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Riset Kesehatan Dasar (Riskesdas) 2013. Jakarta; 2013. https://www.litbang.kemkes.go.id/laporan-riset-nasional/.
Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan Kementerian Kesehatan RI. Hasil Utama RISKESDAS 2018. Jakarta; 2018. https://www.litbang.kemkes.go.id/laporan-riset-nasional/.
Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Laporan Provinsi Jawa Barat, Riskesdas 2018. Lembaga Penerbit Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan. Jakarta: Lembaga Penerbit Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan; 2019. https://www.litbang.kemkes.go.id/laporan-riset-nasional/.
Leal J, Morrow LM, Khurshid W, Pagano E, Feenstra T. Decision models of prediabetes populations: A systematic review. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21(7):1558–69. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30828927. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6619188. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13684.
Noble D, Mathur R, Dent T, Meads C, Greenhalgh T. Risk models and scores for type 2 diabetes: Systematic review. BMJ. 2011;343:d7163. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22123912. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3225074. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d7163.
Lim NK, Park SH, Choi SJ, Lee KS, Park HY. A risk score for predicting the incidence of type 2 diabetes in a middle-aged Korean cohort - The Korean Genome and epidemiology study. Circ J. 2012;76(8):1904–10. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22640983. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.cj-11-1236.
Sharkia R, Sheikh-Muhammad A, Mahajnah M, Khatib M, Zalan A. Exploration of risk factors for type 2 diabetes among arabs in Israel. Ann Glob Heal. 2019; 85(1):67. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31074599. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6634318. https;//doi.org/10.5334/aogh.2350.
Lindström J, Tuomilehto J. The diabetes risk score: A practical tool to predict type 2 diabetes risk. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(3):725–31.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12610029. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.26.3.725.
Zhang H, Wang C, Ren Y, et al. A risk‐score model for predicting risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a rural Chinese adult population: A cohort study with a 6‐year follow‐up. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2017;33(7). https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28608942. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.2911.
Chen X, Wu Z, Chen Y, et al. Risk score model of type 2 diabetes prediction for rural Chinese adults: The Rural Deqing Cohort Study. J Endocrinol Invest. 2017;40(10):1115-23. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28474301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-017-0680-4.
Zhang HY, Shi WH, Zhnag M, et al. Establishing a non-invasive prediction model for type 2 diabetes mellitus based on a rural Chinese population. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016;50 (5):397–403. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27141894. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2016.05.003.
Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Pedoman Pengukuran dan Pemeriksaan Studi Kohor Penyakit Tidak Menular; 2010. https://www.litbang.kemkes.go.id/layanan-perpustakaan/.
American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(Suppl 1):S13–28. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30559228. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-S002.
American Diabetes Association. Updates to the standards of medical care in diabetes-2018. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(9):2045–7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30135199. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc18-su09.
Siswosudarmo R. Tes diagnostik (Diagnostic test). J Metodol Penelit [Internet]. 2017. http://obgin-ugm.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/HRS-Kuliah-Tes-Diagnostik.pdf.
Sastroasmoro S, Ismael S. Dasar-dasar metodologi penelitian klinis, 3rd ed. Jakarta: Sagung Seto; 2008.
Putra IWG. Sutarga IM. Kardiwinata MP. Suariyani NLP. Septarini NW, Subrata I. Modul Penelitian Uji Diagnostik dan Skrining [Internet]. 2016. https://simdos.unud.ac.id/uploads/file_pendidikan_1_dir/d204d4a5ad0870a0965416e671a38791.pdf.
Aekplakorn W, Bunnag P, Woodward M, et al. A risk score for predicting incident diabetes in the Thai population. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(8):1872–7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16873795. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc05-2141.
Sulaiman N, Mahmoud I, Hussein A, et al. Diabetes risk score in the United Arab Emirates: A screening tool for the early detection of type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2018;6(1):e000489. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29629178. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5884268. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjdrc-2017-000489.
Bang H, Edwards AM, Bomback AS, et al. Development and validation of a patient self-assessment score for diabetes Risk. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(11):775-83. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19949143. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3633111. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-151-11-200912010-00005.
Chen L, Magliano DJ, Balkau B, et al. AUSDRISK: An Australian type 2 diabetes risk assessment tool based on demographic, lifestyle and simple anthropometric measures. Med J Aust. 2010;192(4):197–202. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20170456. https://doi.org/10.5694/j.1326-5377.2010.tb03507.x.
Glümer C, Carstensen B, Sandbaek A, Lauritzen T, Jorgensen T, Borch-Johnsen K. A Danish diabetes risk score for targeted screening. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(3):727–33. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14988293. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.27.3.727.
Al-Lawati JA, Tuomilehto J. Diabetes risk score in Oman: A tool to identify prevalent type 2 diabetes among Arabs of the Middle East. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;77(3):438–44. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17306410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2007.01.013.
Gao WG, Dong YH, Pang ZC, et al. A simple Chinese risk score for undiagnosed diabetes. Diabet Med. 2010;27(3):274–81. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20536489. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2010.02943.x.
Mohan V, Deepa R, Deepa M, Somannavar S, Datta M. A simplified Indian Diabetes Risk Score for screening for undiagnosed diabetic subjects. J Assoc Physicians India. 2005;53:759–63. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16334618.
American Diabetes Association. Are you at risk for type 2 diabetes? 2009. http://main.diabetes.org/dorg/PDFs/risk-test-paper-version.pdf.
Pertiwi MD. Identifikasi Pengetahuan Ibu Hamil Dalam Manajemen Penyakit Diabetes Mellitus Gestasional Di Puskesmas Minggir Yogyakarta; 2019.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
The full license is at this link: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/legalcode).
To obtain permission to translate/reproduce or download articles or use images FOR COMMERCIAL REUSE/BUSINESS PURPOSES from the Journal of the ASEAN Federation of Endocrine Societies, kindly fill in the Permission Request for Use of Copyrighted Material and return as PDF file to jafes@asia.com or jafes.editor@gmail.com.
A written agreement shall be emailed to the requester should permission be granted.










