Initiating or Switching to Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes in Malaysia
Results from a Prospective, Non-Interventional Real-World Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15605/jafes.038.01.12Keywords:
Type 2 diabetes mellitus, insulin degludec, insulin aspart, Malaysia, hypoglycemiaAbstract
Objectives. Insulin degludec (IDeg)/insulin aspart (IAsp; IDegAsp) is a co-formulation of 70% IDeg and 30% IAsp. According to several randomized controlled trials, IDegAsp is effective and safe for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). A subgroup analysis of the ARISE study was conducted to explore the safety and efficacy of IDegAsp among Malaysian patients with T2DM in real-world settings.
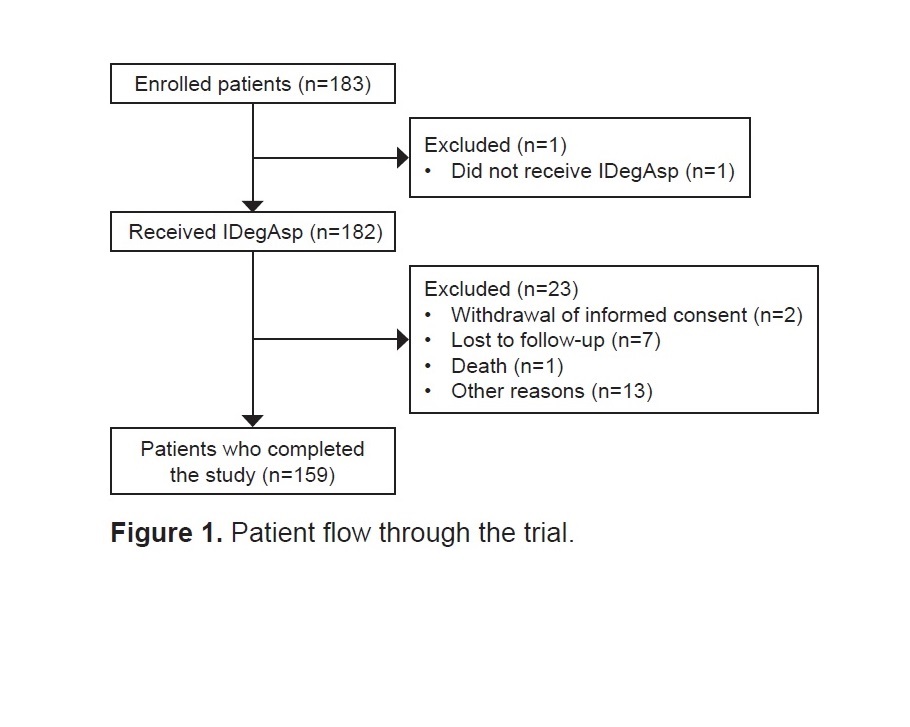
Methodology. ARISE, an open-label, multicenter, non-interventional, prospective study was conducted between August 2019 and December 2020. Adult Malaysian patients with T2DM who were enrolled from 14 sites received IDegAsp as per the local label for 26 weeks. The primary endpoint was change in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels from baseline
to end of study (EOS).
Results. Of the 182 patients included in the full analysis set, 159 (87.4%) completed the study. From baseline to EOS, HbA1c (estimated difference [ED]: –1.3% [95% CI: –1.61 to –0.90]) and fasting plasma glucose levels (ED: –1.8 mmol/L [95% CI: –2.49 to –1.13]) were significantly reduced (p<0.0001). The patient-reported reduced hypoglycemic episodes (overall and nocturnal) during treatment. Overall, 37 adverse events were observed in 23 (12.6%) patients.
Conclusion. Switching or initiating IDegAsp treatment resulted in significant improvements in glycemic control and a reduction in hypoglycemic episodes.
Downloads
References
IDF Diabetes Atlas, Diabetes around the world in 2021. 2021. https://diabetesatlas.org/. Accessed May 9, 2022.
Malaysia MoH. Fact sheet: National health and morbidity survey 2019, non-communicable diseases, healthcare demand, and health literacy. 2019. https://iku.gov.my/images/IKU/Document/REPORT/NHMS2019/FactSheet_BI_AUG2020.pdf. Accessed May 6, 2022.
Syed Soffian SS, Ahmad SB, Chan HK, Soelar SA, Abu Hassan MR, Ismail N. Management and glycemic control of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at primary care level in Kedah, Malaysia: A statewide evaluation. PLoS One. 2019;14(10):e0223383. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31581261. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6776298. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0223383.
Malaysia MoH. Clinical practice guidelines: Management of type 2 diabetes mellitus, 6th edition. 2020. https://www.moh.gov.my/moh/resources/Penerbitan/CPG/Endocrine/QR_T2DM_6th_Edition_QR_Guide_Digital.pdf. Accessed May 3, 2022.
Peyrot M, Barnett AH, Meneghini LF, Schumm-Draeger PM. Insulin adherence behaviours and barriers in the multinational global attitudes of patients and physicians in insulin therapy study. Diabet Med. 2012;29(5):682-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22313123. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3433794. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2012.03605.x.
Franek E, Haluzík M, Canecki Varžić S, et al. Twice-daily insulin degludec/insulin aspart provides superior fasting plasma glucose control and a reduced rate of hypoglycaemia compared with biphasic insulin aspart 30 in insulin-naïve adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2016;33(4):497-505. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26435365. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5063147. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.12982.
Kalra S, Atkin S, Cervera A, et al. Multinational consensus: Insulin initiation with insulin degludec/aspart (IDegAsp). Adv Ther. 2018;35(7):928-36. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29796928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-018-0712-2.
Heise T, Nosek L, Roepstorff C, Chenji S, Klein O, Haahr H. Distinct prandial and basal glucose-lowering effects of insulin degludec/insulin aspart (IDegAsp) at steady state in subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Ther. 2014;5(1):255-65. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24888255. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4065302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-014-0070-2.
Fulcher GR, Jarlov H, Piltoft JS, et al. ARISE-a prospective, non-interventional, single-arm study assessing clinical parameters associated with the use of insulin degludec/insulin aspart in patients with type 2 diabetes in real-world settings: Rationale and design. Endocrine. 2021;74(3):530-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34637072. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8506473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02887-8.
Rodbard HW, Cariou B, Pieber TR, Endahl LA, Zacho J, Cooper JG. Treatment intensification with an insulin degludec (IDeg)/insulin aspart (IAsp) co-formulation twice daily compared with basal IDeg and prandial IAsp in type 2 diabetes: a randomized, controlled phase III trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016;18(3):274-80. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26592732. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5066701. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.12609.
Fulcher GR, Christiansen JS, Bantwal G, et al. Comparison of insulin degludec/insulin aspart and biphasic insulin aspart 30 in uncontrolled, insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a phase 3a, randomized, treat-to-target trial. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(8):2084-90. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24812432. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc13-2908
Gerety G, Bebakar WM, Chaykin L, et al. Treatment intensification with insulin degludec/insulin aspart twice daily: Randomized study to compare simple and step-wise titration algorithms. Endocr Pract. 2016;22(5):546-54. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26720250. https://doi.org/10.4158/ep15893.
Hirsch IB, Franek E, Mersebach H, Bardtrum L, Hermansen K. Safety and efficacy of insulin degludec/insulin aspart with bolus mealtime insulin aspart compared with standard basal-bolus treatment in people with type 1 diabetes: 1-year results from a randomized clinical trial (BOOST(®) T1). Diabet Med. 2017;34(2):167-73. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26773446. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5248618. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.13068.
Kaneko S, Chow F, Choi DS, et al. Insulin degludec/insulin aspart versus biphasic insulin aspart 30 in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on basal or pre-/self-mixed insulin: A 26-week, randomised, treat-to-target trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;107(1):139-47. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25498130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2014.09.026.
Haluzík M, Fulcher G, Pieber TR, Bardtrum L, Tutkunkardas D, Rodbard HW. The co-formulation of insulin degludec and insulin aspart lowers fasting plasma glucose and rates of confirmed and nocturnal hypoglycaemia, independent of baseline glycated haemoglobin levels, disease duration or body mass index: A pooled meta-analysis of phase III studies in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20(7):1585-92. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29451706. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6033009. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.13261.
Fulcher GR, Akhtar S, Al-Jaser SJ, et al. Initiating or Switching to Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Real-World, Prospective, Non-interventional Study Across Six Countries. Adv Ther. 2022:1-14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-022-02212-3
Moon S, Chung HS, Kim YJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of insulin degludec/insulin aspart compared with a conventional premixed insulin or basal insulin: A meta-analysis. Metabolites. 2021;11(9):639. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34564455. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8470485. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11090639.
Long T, Lin JT, Lin MH, et al. Comparative efficiency and safety of insulin degludec/aspart with insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Endocr J. 2022;69(8):959-69. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35431280. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.EJ21-0692.
Jang HN, Yang YS, Oh TJ, et al. Low fasting glucose-to-estimated average glucose ratio was associated with superior response to insulin degludec/aspart compared with basal insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2022;13(1):85-93. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34291584. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8756314. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.13634.
Shigiyama F, Liu L, Nordahl H, Suzuki R, Yamamoto Y, Hirose T. A real-world, prospective, non-interventional study of adults with T2D switching to idegasp from glargine U100 or U300 in Japan. Diabetes Ther. 2021;12(9):2405-21. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34304385. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8385001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-021-01117-8.
Hassanein M, Echtay AS, Malek R, et al. Original paper: Efficacy and safety analysis of insulin degludec/insulin aspart compared with biphasic insulin aspart 30: A phase 3, multicentre, international, open-label, randomised, treat-to-target trial in patients with type 2 diabetes fasting during Ramadan. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;135:218-26. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29183844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2017.11.027
Kalra S, Czupryniak L, Kilov G, et al. Expert opinion: Patient selection for premixed insulin formulations in diabetes care. Diabetes Ther. 2018;9(6):2185-99. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30390228. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6250631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-018-0521-2.
Katabami T, Eriksen KT, Yamamoto Y, Ishigaki Y. Long-term safety and clinical outcomes with insulin degludec/insulin aspart treatment in Japanese patients with diabetes: A real-world, prospective, observational study. Adv Ther. 2022;39(1):544-61. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34800283. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8799571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-021-01978-2.
Fulcher G, Mehta R, Fita EG, Ekelund M, Bain SC. Efficacy and safety of IDegAsp versus BIAsp 30, both twice daily, in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: Post hoc analysis of two phase 3 randomized controlled BOOST Trials. Diabetes Ther. 2019;10(1):107-18. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30474818. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6349271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-018-0531-0.
Aso Y, Takada Y, Tomotsune K, et al. Comparison of insulin degludec (IDeg)/insulin Aspart (IAsp) co-formulation therapy twice-daily with free combination of GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide plus insulin degludec in Tochigi: IDEAL Trial. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75(4):e13734. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33099848. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcp.13734.
Topaloğlu US, Topaloğlu HK, Kızıltepe M, et al. Fear of hypoglycemia in adults with diabetes mellitus switching to treatment with IDegAsp co-formulation to examine real-world setting: an observational study (The HATICE study). Drug Metab Pers Ther. 2020. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33780195. https://doi.org/10.1515/dmdi-2020-0166
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Mafauzy Mohamed, Siang Chin Lim , Malik Mumtaz, Shweta Uppal, Deepak Mukherjee, Mohamed Saiful Mohd Kassim, Shalini Sreedharan, Amudha Murugan Doraiswamy, Kuck Meng Chong, Lu Yu Tat, Sudzilla Binti Nordin, Jeshen Lau Hui Giek, Zanariah Hussein, Khalid Abdul Kadir, Bik Kui Lau, Siew Pheng Chan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The full license is at this link: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/legalcode).
To obtain permission to translate/reproduce or download articles or use images FOR COMMERCIAL REUSE/BUSINESS PURPOSES from the Journal of the ASEAN Federation of Endocrine Societies, kindly fill in the Permission Request for Use of Copyrighted Material and return as PDF file to jafes@asia.com or jafes.editor@gmail.com.
A written agreement shall be emailed to the requester should permission be granted.










